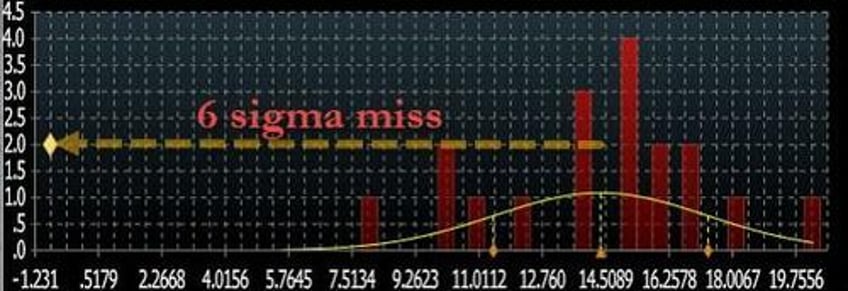
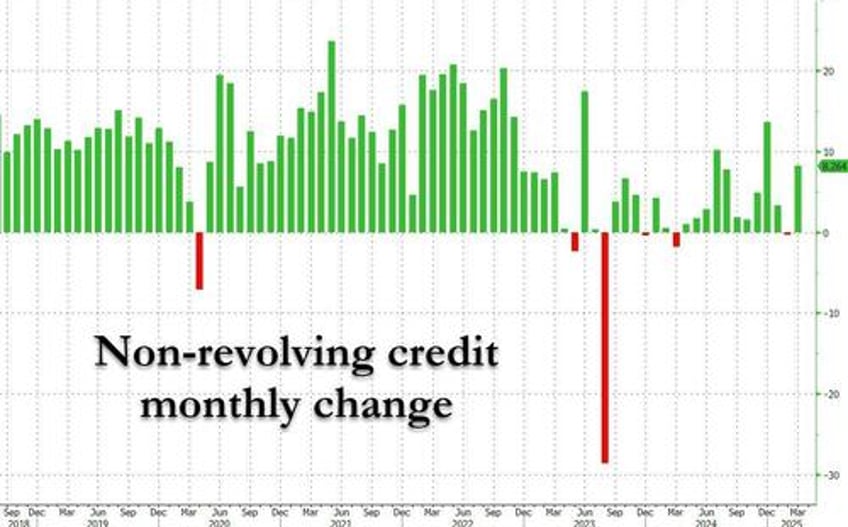
One month ago, just as our long-running narrative that US consumers had been living with maxed out credit cards for the past year was becoming mainstream, the Fed's February consumer credit data confirmed as much: a huge, 6-sigma miss to expectations of a $15BN print, when the actual number came in at a negative $1BN (and far below the lowest estimate)....
... as a result of both Revolving and non-revolving credit coming in flat or negative.
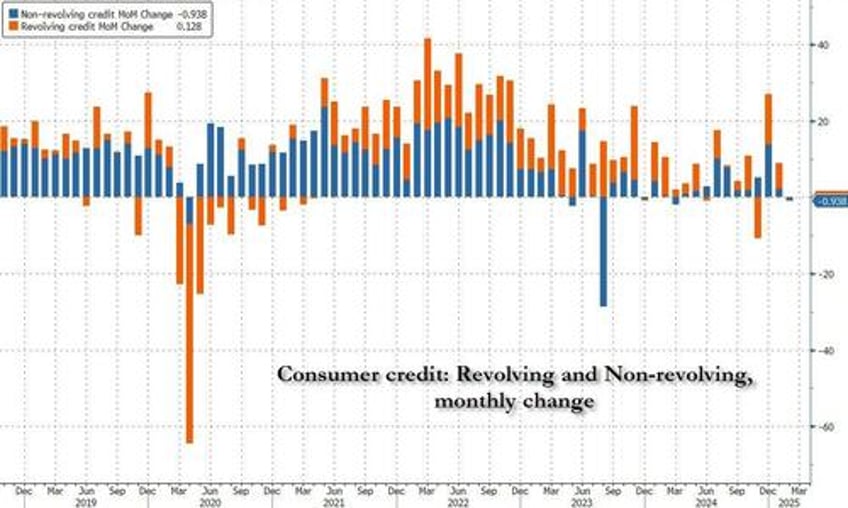
Fast forward to today when amid rising hopes that we would finally get some trend in the soft credit data, the Fed reported that in March, consumer credit... spiked right back to normal, if largely on the back on non-revolving credit. As shown in the chart below, after February $0.6BN contraction, in March consumer credit rose by $10.2BN, just above the $9.4BN expected, and the first time in months consumer credit wasn't a shock outlier either up or down.
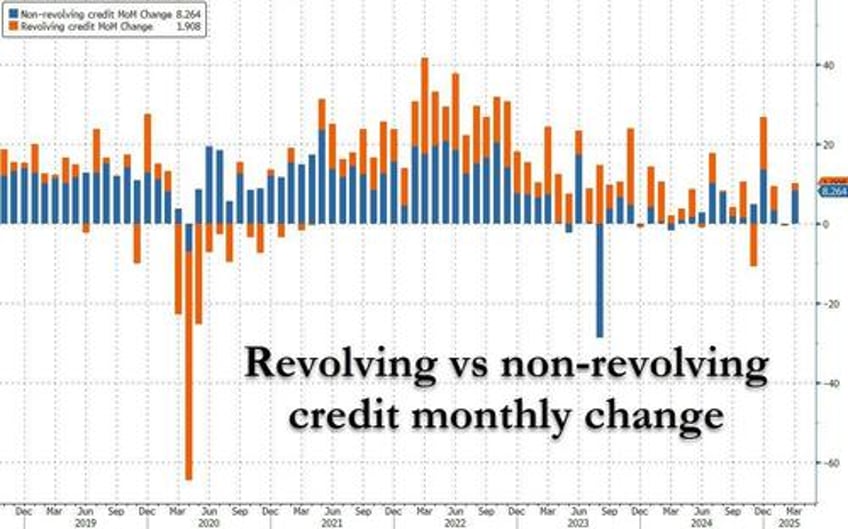
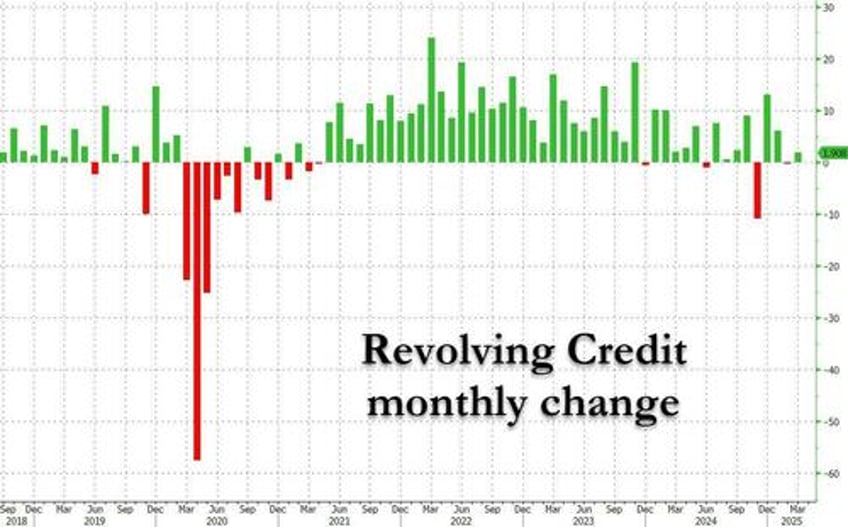
The composition was familiar: revolving credit (i.e., credit card debt) rose by a modest $1.9BN, better than the $0.3BN drop in February, but excluding that, the lowest print since December.
Meanwhile, non-revolving credit jumped by $8.3 billion, the second highest monthly increase since July 2024.
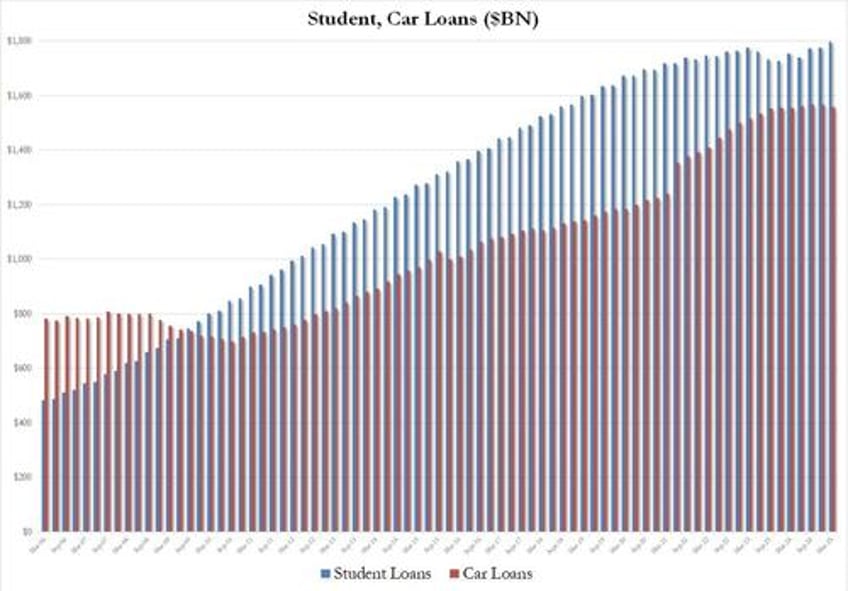
Why? Well, the answer is rather bizarre because while auto loans shrank by $10 billion in Q1, the biggest quarterly decline in a decade, it was student debt, that debt which is now causing widespread defaults as millions can not afford to pay it as the moratorium is over, that unexpectedly surged by $22BN in Q1 to $1,797 billion, a new all time high.
How realistic is it that in a time when millions of former "students" are about to start defaulting en masse, that it is student loans which are again propelling consumer spending, we keep a close eye on this series because while many expect that the student loan bubble bursting will accelerate the recession, we may be getting just the opposite as Trump takes another page from the Biden playbook and starts firehosing "student" loans to anyone with a pulse who can fog a mirror.